Error handling in the Abaqus Scripting Interface¶
The basics of Python’s exception handling apply to the Abaqus Scripting Interface. Python’s exception handling is described in Error handling. If certain circumstances arise while a script is running, Python allows you to take the necessary action and still allows the script to continue. Alternatively, when Abaqus/CAE issues (or “throws”) an exception and the exception is not handled by the script, Abaqus/CAE displays the exception message in the message area and the script stops executing.
Standard Python exceptions¶
Python exceptions arise from either system-related problems, such as a disk or network error, or from programming errors, such as numeric overflow or reference to an index that does not exist. Standard Python exceptions are not described in this guide and are not listed as possible exceptions in the Abaqus Class References.
Look at the standard Python documentation on the official Python website (https://www.python.org) for a list of standard Python exceptions. Standard exceptions are described in the Built-in Exceptions section of the Python Library Reference.
Standard Abaqus Scripting Interface exceptions¶
Standard Abaqus Scripting Interface exceptions arise from errors in a script that relate to Abaqus/CAE. The standard Abaqus Scripting Interface exceptions that can be raised by a method are listed with each command in the Abaqus Class References.
The standard Abaqus Scripting Interface exception types are listed below:
InvalidNameError
You specified an invalid name. Abaqus/CAE enforces a naming convention for objects that you create. Names must adhere to the following rules:
Part, model, instance, set, surface, feature, and job names can have up to 80 characters; other object names can have up to 38 characters. Instance names of models that have been instantiated as model instances in another model still have a 38-character limit. For imported sets/surfaces, parts, and model instances, the names are generated internally in Abaqus/CAE by combining part/instance/set names. You must ensure that the combined length will not exceed 80 characters; otherwise, the data check analysis will fail.
The name can include spaces and most punctuation marks and special characters; however, only 7-bit ASCII characters are supported.
警告
While Python allows most punctuation marks and special characters, some of the strings you provide will be used in an Abaqus input file; therefore, you cannot use the following characters:
\$\&\*\~\!\(\)\[\]\{\}\|\;\'\`\"\,\.\?\/\\when you are naming an object, such as a part, a model or a job.The name must not begin with a number.
The name must not begin or end with an underscore or a space.
The name must not contain a period or a double quote.
RangeError
A numeric value is out of range.
AbaqusError
Context-dependent message.
AbaqusException
Context-dependent message.
备注
The command descriptions in the Abaqus Class References list the type of standard Abaqus Scripting Interface exceptions that can occur; however, the exception messages are not included with the command description.
Additional Abaqus Scripting Interface exceptions¶
Each command in the Abaqus Class References lists the standard Abaqus Scripting Interface exceptions that can be raised by a command. In addition, if the exception is not a standard Python or Abaqus Scripting Interface exception, the description lists the following:
A brief description of the problem.
The exception type.
The exception message.
For example, 图 8 shows the layout of a typical exception description in the online documentation.
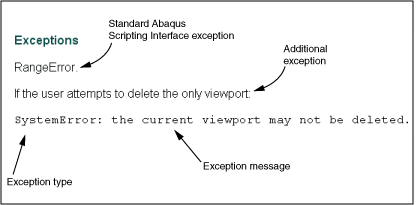
图 8 The layout of a typical exception description in the online documentation.¶
You use the exception type in your error handling routines.
Exception handling¶
The Python exception handling techniques described in Error handling apply to the Abaqus Scripting Interface. You should use the command description in the Abaqus Class References to decide for which exception types you need to account. For example, the following Abaqus Scripting Interface script attempts to create a viewport and prints a message if the width or height are too small:
The resulting output is
Viewport too small: width must be a Float >= 30
Script continues running and prints this line
The exception has been handled, and the script continues.